We’ll discover how to create a basic calculator using Python. Feel free to utilize any online Python environment to write the code. I typically use this one: https://programiz.pro/ide/python.
Python’s straightforward syntax and clear structure make it perfect for developing a calculator application. This project will provide insight into essential concepts such as user input handling, conditional statements, and fundamental arithmetic operations.
The Code
num1 = float(input("Enter first number: "))
operator = input("Enter operator (+, -, *, /): ")
num2 = float(input("Enter second number: "))
if operator == "+":
result = num1 + num2
elif operator == "-":
result = num1 - num2
elif operator == "*":
result = num1 * num2
elif operator == "/":
result = num1 / num2
else:
result = "Invalid operator"
print("Result:", result)Explanation
To understand this program. Let’s break it down into a few parts to understand it.
Part One: User Input

This section takes in the user input using the “input" function. The “float" function is used to convert the input into floating-point numbers, which allows for both integer and decimal inputs. The users will be asked to enter the first number, then an operator (+, -, *, /), and finally a second number.
Part Two: Conditional Statements
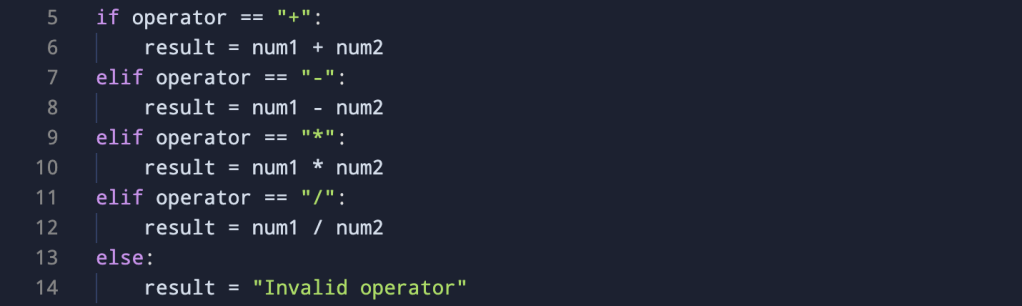
Lines 5 – 14 capture the conditional statements of the program. This block utilizes conditional statements to evaluate the entered operator and perform the corresponding arithmetic operation. If the operator is addition (+), the program adds the two numbers; if it’s subtraction (-), it subtracts the second number from the first, and so on. If the entered operator is not one of these, the program will set the result to say “Invalid Operator”.
if operator == "+":- If the entered operator is addition (
+), the program executes the block of code indented under this “if” statement. It calculates the sum ofnum1 andnum2and assigns the result to the variableresult.
- If the entered operator is addition (
elif operator == "-":- If the
ifstatement above is not true (i.e., the operator is not+), the program checks thiselif(else if) statement. If the operator is subtraction (-), it executes the corresponding block, subtractingnum2fromnum1and assigning the result toresult.
- If the
elif operator == "*":- Similarly, if the previous conditions are not met, this
elifstatement checks whether the operator is multiplication (*). If true, it calculates the product ofnum1andnum2and assigns the result toresult.
- Similarly, if the previous conditions are not met, this
elif operator == "/":- This
elifstatement handles the case of division (/). If the operator is/, it performs the division ofnum1bynum2and assigns the result toresult.
- This
else:- If none of the preceding
iforelifconditions are true (i.e., the entered operator is not+,-,*, or/), the program executes theelseblock. In this case, it setsresultto “Invalid operator,” indicating that the entered operator is not recognized.
- If none of the preceding
Part Three: Output

The “print” statement displays the result of the calculation to the user. If a valid operator was entered, the result is shown; otherwise, a message will return saying “Invalid Operator”.
Demonstration
Here is a quick demonstration of the program when it is executed.
The program will first ask the user to enter a number

Next, an operator will be selected
After that, you will enter the second number

Finally, the result will be displayed
